Table of Content
- How do I change the PATH variable in Windows 10?
- Add Directories to PATH Variable
- Set ORACLE_HOME environment variable on Windows
- Assignment: DOS, OS/2 and Windows
- List of All Environment Variables in Windows 10
- Install Oracle 19c Database On Windows 10
- How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
Setting the PATH variable for a program or command allows you to run it from anywhere on the system without having to specify its absolute path. The path is based on programs installed on the computer, so there is no "default path." However, the Windows minimum path is often the path below. In the About window, click the Advanced system settings link under Related settings on the far-right side. Chances are, if you’re reading this, you’ve run into something that requires you to add it to the PATH variable, so that’s probably what you should do. If you just want to add something to your PATH for easier access, though, that’s also fine.
Use these environment variables to browse Windows 10 locations on any computer quickly. Now that you know a bunch of Windows 10 environment variables, you might be wondering how to use these environment variables. Actually, there are quite a few ways you can use these environment variables. I’ll show two of the most common ways to use the environment variables to open the relevant folders. Windows 10 has several such environment variables that make your life easier. Below is the list of all useful environments variable in Windows 10.
How do I change the PATH variable in Windows 10?
These are values that are fetched like environment variables, but are not truly stored in the environment but computed when requested. %$WIDTH%Used by DOS Plus to define the screen width of the console in columns. This is used to control in a portable way the formatting of the screen output of commands like DIR /W or TYPE filename. See also the related environment variables %$LENGTH% and %DIRSIZE% as well as the similar pseudo-variable %_COLUMNS%.

It is possible to specify relative directories here, including "." for the current working directory. See also the related environment variable %ENDLIBPATH%. While they can be used in batch jobs and at the prompt, they are not stored in the environment.
Add Directories to PATH Variable
Shortcut links copied to the All Users\' Start menu or Desktop directories will appear in every user's Start menu or Desktop, respectively. An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. %STATION%This pseudo-variable returns the logical station number starting with "1" for the first client. The numbers are assigned by the file server and remain static for as long as the IPX connection remains established. %YEAR% and %_YEAR%Supported since Novell DOS 7, the %YEAR% pseudo-variable returns the year of the current date in a 4-digit format, f.e.
Open a new command-prompt window and test your program by typing in the name of the executable you want to launch. It won’t work in the current window since it’s still using the old PATH variable. Open a Command Prompt window (Win⊞ + R, type cmd, hit Enter). This should output the path to your Java installation folder. %LOGIN_NAME%This pseudo-variable returns the user name.
Set ORACLE_HOME environment variable on Windows
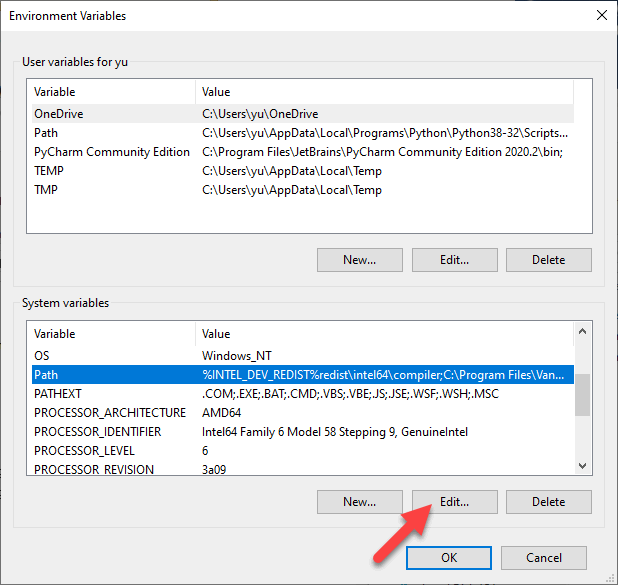
Note that you can also move items up and down on the list. When you type a command at the command prompt, Windows has to search through each directory stored in the PATH variable to see if that executable exists or not. If you want your executable to be found faster, just move that path up to the top of the list.

%TASKMGRWINDIR%This variable specifies the directory, where the Windows SYSTEM.INI to be used by the DR-DOS TASKMGR multitasker is located, overriding the default procedure to locate the file. It can be in several formats, either specifying the time zone itself or referencing a file (in /usr/share/zoneinfo). WikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
Consequently, they are neither listed by SET nor do they exist for external programs to read. %PATH%This variable contains a semicolon-delimited list of directories in which the command interpreter will search for an executable file that matches the given command. Environment variables that represent paths may be nested within the %PATH% variable, but only at one level of indirection. If this sub-path environment variable itself contains an environment variable representing a path, %PATH% will not expand properly in the variable substitution. PATH is an environment variable on Unix-like operating systems, DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, specifying a set of directories where executable programs are located.
Unless you want to potentially destroy your PC's system, DO NOT edit this variable unless you know what you're doing. Create these doskey macros, somewhere they get picked up every time cmd starts up. %LocalAppData% seems to be added in Vista; older versions have the directory but it can be only found using the shell API, not envvars. When I try to create a folder with mkdir %HomeDrive%%HomePath%/MyFolder on Windows with PowerShell it just creates a folder with that literal name including percent signs. To add a new path, simply click on New and it’ll add a new line to the bottom of the list. If you know the path, simply type it in or copy and paste it.
For this reason, libc unsets these environment variables at startup in a setuid process. Setuid programs usually unset unknown environment variables and check others or set them to reasonable values. In Unix, the environment variables are normally initialized during system startup by the system init startup scripts, and hence inherited by all other processes in the system. Users can, and often do, augment them in the profile script for the command shell they are using.

%OS_VERSION%This pseudo-variable returns the version of the operating system depending on the current setting of the environment variable %VER%. If %VER% is not defined, %OS_VERSION% returns "off". It resembles an identically named identifier variable in Novell NetWare login scripts, which may return versions also for non-DR-DOS versions of DOS. By default, most of these programs will add their own custom shortcuts to the Windows environment variables. The most used environment variable in Windows is probably the PATH variable. It basically allows you to run any executables that are located inside the paths specified in the variable at the command prompt without having to give the full path to the executable.
In order to complete those tasks, you most likely have to use a command from a library or software package installed on your system. After creating or modifying the environment variables, restart the computer for those changes to take effect in Windows. You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit.
$LANG, $LC_ALL, $LC_...$LANG is used to set to the default locale. For example, if the locale values are pt_BR, then the language is set to Portuguese and Brazilian practice is used where relevant. Different aspects of localization are controlled by individual $LC_-variables ($LC_CTYPE, $LC_COLLATE, $LC_DATE etc.). $LC_ALL can be used to force the same locale for all aspects.
Oracle Install on Windows:
It is most suitable for the RESTful web service where the URL contains some value. Spring MVC allows us to use multiple @PathVariable annotations in the same method. A path variable is a critical part of creating rest resources. In the System Properties window, choose the Advanced tab. 4DOS and MS-DOS 7.0 set the length to 127 and insert ASCII-13 at this position, but Borland libraries set the length to the invalid value of 128 and do not insert an ASCII-13. For shorter command lines, 4DOS/NDOS and DR-DOS also insert an ASCII-0 after the ASCII-13, but not when invoked vis INSTALL directive; MS-DOS doesn't.