Table of Content
Note that you can also move items up and down on the list. When you type a command at the command prompt, Windows has to search through each directory stored in the PATH variable to see if that executable exists or not. If you want your executable to be found faster, just move that path up to the top of the list.
External commands and some internal commands set error levels upon execution. See also the identically named pseudo-variable %ERRORLEVEL% under DR-DOS and the IF ERRORLEVEL command. %_MINUTE%This pseudo-variable returns the minutes of the current time without leading zeros, f.e "0".."59". %_CODEPAGE%This pseudo-variable returns the systems' current code page ("1".."65533"), f.e. %PROMPT% (supported since DOS 2.0)This variable contains a $-tokenized string defining the display of the prompt. $BROWSERContains a colon-separated list of a user's web browser preferences, for use by programs that need to allow the user to view content at a URL.
What is Windows PATH and How Do You Add to and Edit it?
%$LENGTH%Used by DOS Plus to define the screen length of the console in lines. See also the related environment variables %$WIDTH% and %DIRSIZE% as well as the similar pseudo-variable %_ROWS%. %DIRCMD% (supported since MS-DOS 5.0 and PC DOS 5.0, also supported by ROM-DOS)Allows a user to specify customized default parameters for the DIR command, including file specifications.
%_COUNTRY%This pseudo-variable returns the systems' current country code ("1".."65534"), f.e. "1" for USA, "44" for UK, "49" for Germany, "20049" with ISO 8601, "21049" with ISO 8601 and Euro support. %ERRORLEVEL%In COMMAND.COM of DR-DOS 7.02 and higher, this pseudo-variable returns the last error level returned by an external program or the RETURN command, f.e. See also the identically named pseudo-variable %ERRORLEVEL% under Windows and the IF ERRORLEVEL conditional command. %LOCALAPPDATA%This variable is the temporary files of Applications. Its uses include storing of desktop themes, Windows error reporting, caching and profiles of web browsers.
How do I change the path variable in Windows?
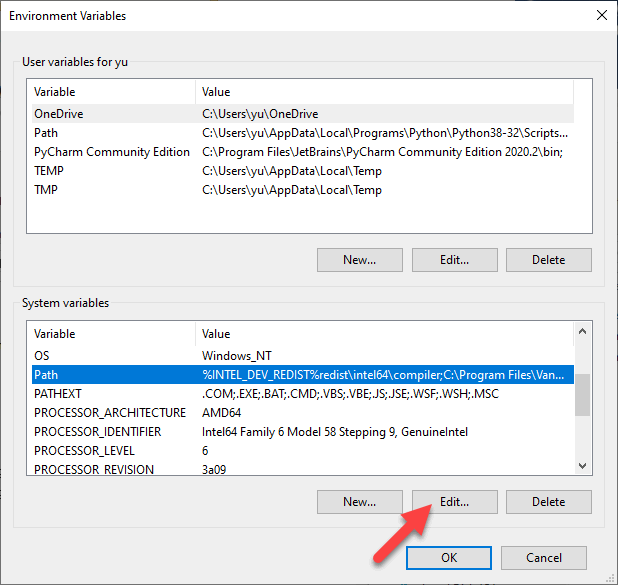
In the Environment Variables window, click on the Path variable name from either section and hit the Edit button. On Windows 7 and Windows 8, add a semi-colon at the end of the line, and without leaving a space, paste the program’s path you just copied into the Path field. Typically, when you have to launch a program or execute a command, you have two options. Either you can navigate to the directory where the program/command is stored and execute it from there. Or, you can use the absolute path for that program/command in the file system to run it from anywhere. %ERRORLEVEL%This pseudo-variable expands to the last set error level, a value between "0" and "255" .

In Microsoft Windows, each environment variable's default value is stored in the Windows Registry or set in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file. The path is now managed by Windows 2000 and Windows XP and not the autoexec.bat or autoexec.nt files, as was done with earlier versions of Windows. To change the system environment variables, follow the steps below. On Windows 10, environment variables are predefined names representing the path to certain locations within the operating system, such as a drive or a particular file or folder. Environment variables are name-value pairs for various programs or processes on an operating system.
What is the version of operating system?
Using the environment variable also gives the user the possibility to point to another directory. The SET command without any arguments displays all environment variables along with their values; SET "0 or more spaces" shows the internal ones too. In CMD.EXE, it is possible to assign local variables that do not leak outside using the SETLOCAL command. The command env displays all environment variables and their values. The command printenv can also be used to print a single variable by giving that variable name as the sole argument to the command.

Stack Exchange network consists of 181 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. From the desktop, right-click My Computer and click Properties. If you don't have a My Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the My Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties. On the desktop, right-click the Computer icon and select Properties. If you don't have a Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties. Ready to keep digging beneath the Windows bonnet?
Assignment: DOS, OS/2 and Windows
Setting this to "ON" has the same affect as adding /P to commands supporting it . Click the New button to add new paths or edit to modify the existing path. You can skip steps 1 to 3 and directly open "System Properties" by pressing Windows+S to open the search menu and typing "environment", and pressing open. Adding a directory to your path makes it possible to run programs from the command line without typing the full path. Keep in mind that some of the variables mentioned are not location-specific, including %COMPUTERNAME%, %PATHEXT%, %PROMPT%, %USERDOMAIN%, %USERNAME%. Oh, also it allows lazy quoting, which I found useful, even when spaces are in the folder path names, since it wraps all of the arguments as if it was one long string.

%MONTH%This pseudo-variable returns the months of the current date in a 2-digit format with leading zeros, f.e. %DAY%This pseudo-variable returns the days of the current date in a 2-digit format with leading zeros, f.e. The command processors in DOS and Windows also support pseudo-environment variables.
%APPEND% (supported since DOS 3.3)This variable contains a semicolon-delimited list of directories in which to search for files. It is usually changed via the APPEND /E command, which also ensures that the directory names are converted into uppercase. Some DOS software actually expects the names to be stored in uppercase and the length of the list not to exceed 121 characters, therefore the variable is best not modified via the SET command. On Unix, a setuid program is given an environment chosen by its caller, but it runs with different authority from its caller. The dynamic linker will usually load code from locations specified by the environment variables $LD_LIBRARY_PATH and $LD_PRELOAD and run it with the process's authority. If a setuid program did this, it would be insecure, because its caller could get it to run arbitrary code and hence misuse its authority.
%HOUR%This pseudo-variable returns the hours of the current time in 12-hour format without leading zeros, f.e. %AM_PM%This pseudo-variable returns the ante- or post-midday status of the current time. The returned string depends on the locale-specific version of DR-DOS, f.e.

No comments:
Post a Comment